Abstract
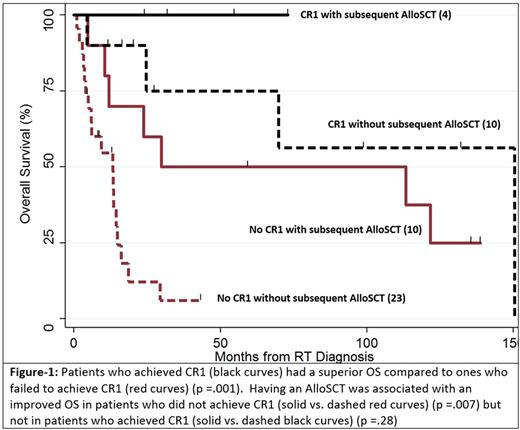
Background: Patients (pts) with RT from CLL have poor long-term outcomes with standard treatments. We examined the pt outcomes and the impact of different treatment options of standard therapy alone, standard therapy followed by autologous (autoSCT) or allogeneic stem cell transplant (alloSCT) or CAR-T cell therapy. Methods: Between 1998 and 2016, 47 pts were identified who had a diagnosis of CLL and transformed to aNHL. Multivariable models were used to test for independent predictors of overall survival (OS) by including the following factors: age at RT diagnosis, presence of del17p, high CD38, high ZAP-70, prior treatment for CLL (none/any), more than 2 treatments for CLL, ibrutinib therapy for CLL, complete response to first line of treatment for RT (CR1), autoSCT, alloSCT and CAR-T cell treatments for RT. Results: Median age at the time of RT diagnosis was 63 (35 - 91) years and 38% of pts were female. High risk CLL features included del17p (32%), del11q (15%), complex karyotype (11%), high CD38 (38%) and high ZAP-70 (28%). Fifteen pts (32%) had required no therapy for CLL before the RT diagnosis. Median number of CLL treatments was 1 (range: 0 -5). Most commonly used CLL treatments were fludarabine-based regimens (57%), bendamustine-based regimens (13%), ibrutinib (11%) and RCHOP (11%). Four percent had received alloSCT for CLL. Median time interval from CLL to RT diagnosis was 26 months (range 0 - 301). For RT therapy, pts received median three lines of treatment (range: 1 - 8). Fourteen pts (30%) achieved CR after first line treatment (CR1). CR1s were achieved using RCHOP (9), REPOCH (4) and HyperCVAD (1). Five patients (11%) received autoSCT only, 7 (15%) had alloSCT only and 7 (15%) received autoSCT followed by alloSCT. Six (13%) had treatment with CAR-T cells. Two of the CAR-T pts also had an autoSCT (1 before and 1 after) and 2 had alloSCT (both before CAR-T treatment). Median follow-up after RT diagnosis was 15 months (0.9 - 150) and median OS was 23.8 months (range 0.9 - 150). Overall, 3-year-OS was 47% (95% CI: 32-60). The 3-year OS rate was significantly higher in patients who achieved CR1: 86% (95% CI: 54-96) vs. 30% (95% CI: 16-46); p =.001. Among pts with CR1, 6 patients subsequently received transplant (autoSCT only= 1, alloSCT only=2, both =3) and all these pts were alive after median follow-up of 43 months (range: 20 -132). Outcome of these pts was not statistically different from those in CR1 who did not have a subsequent transplant (n=8) and had a 3-year OS of 75% (95% CI 31-93); p = .20. On the other hand, in patients who did not achieve CR1, there was a trend towards a better 3-year OS in patients who subsequently received transplant (autoSCT only=3, alloSCT only=6, both, =4) compared to those who did not (n=20): 46% (95% CI: 19-49) vs. 20% (95% CI: 6 -39); p = .05. Among all patients and in a multivariable model, only achievement of CR1 (HR 0.13; p .003) and having an alloSCT (HR 0.28; p 0.02) were associated with an improved OS. Among patients who did not achieve CR1 and in the multivariate analysis, there was a trend for improved OS only in patients who received an alloSCT (HR 0.35; p 0.06). Conclusion: Pts with RT have poor clinical outcome especially if they fail to achieve a CR after first line of treatment. Novel combinations are needed to increase the likelihood of achieving CR1. AlloSCT is associated with an improved OS in those pts and in RT pts in general and should be considered for treatment of RT pts.
Shadman: Pharmacyclics: Other: advisory board, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; PLEXXIKON: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Emergent: Research Funding; AbbVie: Other: advisory board. Till: Genentech: Research Funding; Mustang Bio: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Holmberg: Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; JAZZ: Consultancy; Up To Date: Patents & Royalties. Maloney: Celgene: Other: Advisory board; Juno Theraapeutics: Other: Advisory board, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Roche/Genetech: Other: Advisory board; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Other: Advisory board. Gopal: Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Press: Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria; Bayer: Consultancy. Smith: Genentech: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Sharp: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Dohme Corp: Research Funding; Portola Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.